The Gaussian (Normal) distributions centered on m and width given by 2s. More...
Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| double | LRd_gausbm_RAN (LR_obj *o) |
| LRd_gausbm_RAN(LR_obj *o) - double random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Box-Muller method. More... | |
| double | LRd_gausmar_RAN (LR_obj *o) |
| LRd_gausmar_RAN(LR_obj *o) - double random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Marsaglia method with acceptance-rejection. More... | |
| double | LRd_gaus_PDF (LR_obj *o, double x) |
| LRd_gaus_PDF(LR_obj *o, double x) - double Gaussian/Normal probablity distribution function. More... | |
| double | LRd_gaus_CDF (LR_obj *o, double x) |
| LRd_gaus_CDF(LR_obj *o, double x) - double Gaussian/Normal cumulative distribution function. More... | |
| float | LRf_gausbm_RAN (LR_obj *o) |
| LRf_gausbm_RAN(LR_obj *o) - float random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Box-Muller method. More... | |
| float | LRf_gausmar_RAN (LR_obj *o) |
| LRf_gausmar_RAN(LR_obj *o) - float random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Marsaglia method with acceptance-rejection. More... | |
| float | LRf_gaus_PDF (LR_obj *o, float x) |
| LRf_gaus_PDF(LR_obj *o, float x) - float Gaussian/Normal probablity distribution function. More... | |
| float | LRf_gaus_CDF (LR_obj *o, float x) |
| LRf_gaus_CDF(LR_obj *o, float x) - float Gaussian/Normal cumulative distribution function. More... | |
Detailed Description
The Gaussian (Normal) distributions centered on m and width given by 2s.
The pseudo-random numbers are distributed from a Gaussian or Normal (also Laplace-Gauss) distribution. The mean is given by m and variance = 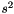 . The normal distribution is a very common continuous probability distribution and is commonly called the bell curve.
. The normal distribution is a very common continuous probability distribution and is commonly called the bell curve.
![\begin{eqnarray*} \mbox{PDF}(x) &= \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi s^2}} e^{-\frac{(x - m)^2}{2 s^2}} \\ \mbox{CDF}(x) &= \frac{1}{2} \left[ 1 + \mbox{erf}\left(\frac{x - m}{s\sqrt{2}}\right) \right] \end{eqnarray*}](form_33.png)
The default is m = 0, s = 1; which is called the standard normal distribution.
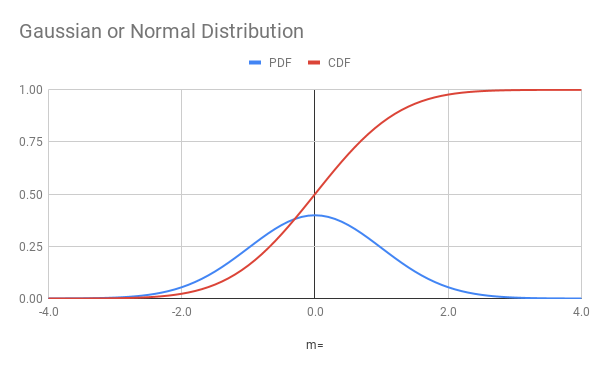
Gaussian distributed random variates can be generated in a couple of methods. The first is the Box-Muller method which generates a pair of Gaussian distributed random variates by considering the 2-dimensional form of the Gaussian distribution. The polar form can yield itself to using the inverse CDF for generating the random variates. However, this requires using time-intensive math functions such as the sin, cos, log, and sqrt functions.
The second method uses the Marsagalia's polar method with acceptance/rejection for generating random variates confined to the unit circle centered on the origin with radius 1. This gives an acceptance ratio to be 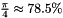 , but the method only uses a single sqrt, log, and division per generated pair. This simplicity may result in a faster generator despite the time to calculate rejected samples.
, but the method only uses a single sqrt, log, and division per generated pair. This simplicity may result in a faster generator despite the time to calculate rejected samples.
Definition in file LRgaus.c.
Function Documentation
◆ LRd_gaus_CDF()
| double LRd_gaus_CDF | ( | LR_obj * | o, |
| double | x | ||
| ) |
LRd_gaus_CDF(LR_obj *o, double x) - double Gaussian/Normal cumulative distribution function.
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object x value
- Returns
- double CDF at x
◆ LRd_gaus_PDF()
| double LRd_gaus_PDF | ( | LR_obj * | o, |
| double | x | ||
| ) |
LRd_gaus_PDF(LR_obj *o, double x) - double Gaussian/Normal probablity distribution function.
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object x value
- Returns
- double PDF at x
◆ LRd_gausbm_RAN()
| double LRd_gausbm_RAN | ( | LR_obj * | o | ) |
LRd_gausbm_RAN(LR_obj *o) - double random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Box-Muller method.
Default values: mean m = 0, std.deviation s = 1
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object
- Returns
- double
◆ LRd_gausmar_RAN()
| double LRd_gausmar_RAN | ( | LR_obj * | o | ) |
LRd_gausmar_RAN(LR_obj *o) - double random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Marsaglia method with acceptance-rejection.
Default values: mean m = 0, std.deviation s = 1
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object
- Returns
- double
◆ LRf_gaus_CDF()
| float LRf_gaus_CDF | ( | LR_obj * | o, |
| float | x | ||
| ) |
LRf_gaus_CDF(LR_obj *o, float x) - float Gaussian/Normal cumulative distribution function.
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object x value
- Returns
- float CDF at x
◆ LRf_gaus_PDF()
| float LRf_gaus_PDF | ( | LR_obj * | o, |
| float | x | ||
| ) |
LRf_gaus_PDF(LR_obj *o, float x) - float Gaussian/Normal probablity distribution function.
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object x value
- Returns
- float PDF at x
◆ LRf_gausbm_RAN()
| float LRf_gausbm_RAN | ( | LR_obj * | o | ) |
LRf_gausbm_RAN(LR_obj *o) - float random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Box-Muller method.
Default values: mean m = 0, std.deviation s = 1
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object
- Returns
- float
◆ LRf_gausmar_RAN()
| float LRf_gausmar_RAN | ( | LR_obj * | o | ) |
LRf_gausmar_RAN(LR_obj *o) - float random Gaussian/Normal distribution using the Marsaglia method with acceptance-rejection.
Default values: mean m = 0, std.deviation s = 1
- Parameters
-
o LR_obj object
- Returns
- float
 1.8.13
1.8.13